- Article
Structure–Activity Relationship and Biosafety of Linear Pentapeptide Analogs Derived from Battacin for Antimicrobial Development
- Haixin Sun,
- Yujie Zhang and
- Chen Yao
- + 1 author
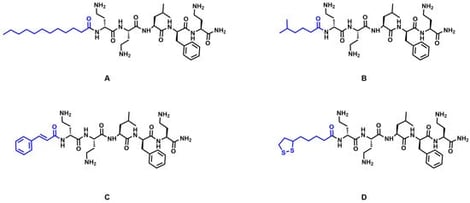
Background: Natural antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) present a promising solution to address the global threat of drug-resistant infections; however, their clinical translation is challenged by limitations in stability, cytotoxicity, and production costs. Methods: In the present study, a linear Battacin-derived peptide (DDLFD) was modified at the N-terminus with lipid chains, cinnamic acid, or lipoic acid. The lipoic acid-modified variant was further crosslinked by UV irradiation to form stable nanoparticles. The antibacterial performance against planktonic and biofilm bacteria was systematically evaluated in vitro. Results: The results demonstrated that lauric acid-modified pentapeptide (C12-5) and crosslinked lipoic acid-modified pentapeptide (cLA-5) exhibited potent and rapid-acting effects against various pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Moreover, they showed enhanced efficacy in eradicating bacterial biofilms. Biosafety assessments based on hemolysis and cytotoxicity assays indicated favorable biocompatibility profiles of cLA-5. Mechanistic investigations confirmed that the modified pentapeptides retained a membrane-targeting mode of action characteristic of natural AMPs, involving membrane depolarization and increased permeability. This physical mechanism effectively prevented the development of resistance in sequential passaging assays and showed strong synergistic effects with ciprofloxacin against ciprofloxacin-resistant strains, effectively restoring their antibiotic susceptibility. Conclusions: Together, these findings underscore the strategic potential of rational structural modification, especially the crosslinked nanostructure, in advancing engineered AMPs toward clinical application.
13 February 2026